Do sheep always need a fluid water source?
This article describes water requirements for sheep during different production stages and environments.

Water is an essential nutrient for life, and it is without question that all animals need water to survive and thrive. As sheep producers, we know our sheep need water, but whether or not they require supplemental, fluid water from a water source is another question which has important implications for how sheep are managed, especially during winter.
The following conditions determine how much supplemental, fluid water is needed by sheep:
- Productive state of the animal – maintenance < growth < pregnancy < lactation
- Environmental temperature and humidity
- Water content of the feed consumed
- How much consumable, frozen water is present (as soft snow!)
These factors together determine the conditions under which sheep need supplemental, fluid water. There are some modifying conditions within each of these major factors to consider as well. This article will consider each condition in turn, which will allow you be better informed of your animal’s water requirements and how to manage supplementation.
Productive state of the animal
Mature ewes and lambs at maintenance (the level of nutrition in which they neither gain nor lose weight) have the lowest water needs compared to the other productive states. Growing animals need more, while sheep in late pregnancy require even more water. The water requirements of early and mid-pregnancy are just slightly more than those at maintenance, then they increase rapidly during the last month of pregnancy (late pregnancy) as nutritional demands of pregnancy accelerate. The extent of this increase in water requirement throughout the stages of pregnancy is also dependent on how many lambs the ewe is carrying. Ewes carrying singles have much lower water requirements than those carrying triplets during late pregnancy. Finally, lactation has the highest water demand compared to the other stages. The specific water needs during lactation are dependent on the extent of the metabolic “burden” of lactation, which in turn is dependent on the stage of lactation and how many lambs the ewe is nursing. So, sheep in early lactation (first 30 days following birth) have higher requirements than those in late lactation (>30 days in milk) because milk production is higher during early stages. Similarly, ewes nursing singles have much lower water requirements than those nursing multiples. As a general rule, ewes carrying twins or greater during late pregnancy, and nearly all ewes in lactation, will require supplemental fluid water, even in cold weather.
Environmental conditions
Without explaining in great detail, it is important to understand that water needs of all livestock drop approximately 50% between 72° and 36° F. Therefore, the water needs of sheep, regardless of productive state, are much lower during winter. In many winter grazing situations it is low enough that their needs can be entirely met with water contained in grazing forage and/or from soft snow. In grazing situations, relative humidity also plays a factor, as the temperature at which dew accumulates on grass (dew point) is directly dependent on humidity (more humid means higher dew point). During fall and spring grazing, as the temperature drops and the air is still relatively humid, there is abundant dew formation on grass which can provide a lot of water to grazing animals. In practice, we find that sheep often ignore water troughs starting in mid-September as the temperature drops and the dew is especially heavy. The same situation holds for early spring, after freezing conditions stop but before temperatures rise significantly.
Water content of feed
The water content of feed is a critical determinant of whether or not sheep need supplemental fluid water. In indoor housing situations with dry feeds, all sheep will need access to a fluid water source, regardless of temperature. In indoor housing situations with silage feeding, this may not be the case, however given the likely need and convenience it is highly advised highly advised to provide water when feeding indoors at all times.In grazing situations however, both need and feasibility change. . Providing supplemental fluid water can be difficult, especially as the temperature drops below freezing. In addition, during cold weather, the water content of many stockpiled forage sources will provide all the water that mature, non-lactating sheep need, as shown in Figure 1.
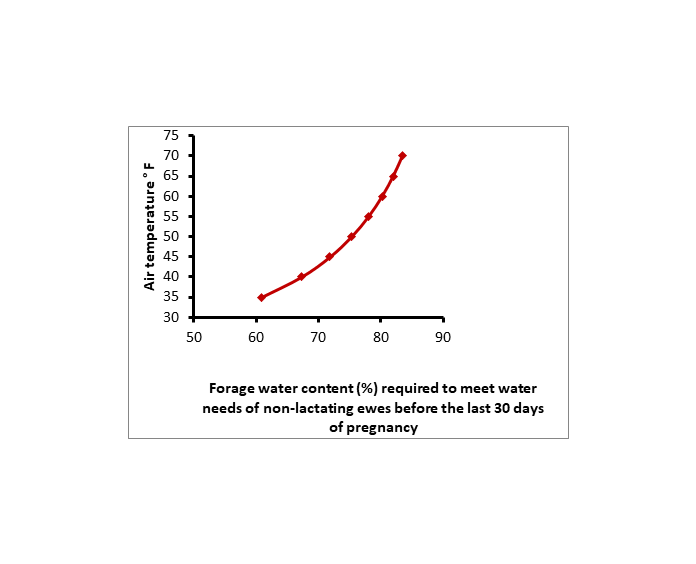 Figure 1. Relationship between forage water content required to meet water needs of non-lactating sheep before late pregnancy and air temperature. Extrapolated from: Forbes 1968, British Journal of Nutrition 22:33-43.
Figure 1. Relationship between forage water content required to meet water needs of non-lactating sheep before late pregnancy and air temperature. Extrapolated from: Forbes 1968, British Journal of Nutrition 22:33-43.For grazing, non-lactating ewes before late pregnancy on cover crops such as brassicas and small grains (forage water content is usually >80%) or in situations of grazing stockpiled perennial pasture (forage water content is usually >70%) during fall and winter, there is no need for fluid water access. This should come as a relief to those contemplating fall and winter grazing and thinking they need a portable, heated stock tank on pasture or some type of frost-free watering system on pasture. In addition, it should confirm the observations of seasoned graziers who already know that if you provide stock tanks filled with fluid water, they will rarely be visited under these conditions.
Based on these examples, it should become clear that it is important to know the forage water content of pasture when grazing during the fall and winter. Those grazing cornstalks or other relatively dry crop residues may have issues providing sufficient water to their sheep without providing a fluid water source. This situation can occur during late fall before snow falls. Once snow accumulates, however, most sheep (excluding lactating and late-pregnant ewes) will be able to obtain sufficient water to meet their needs through snow consumption.
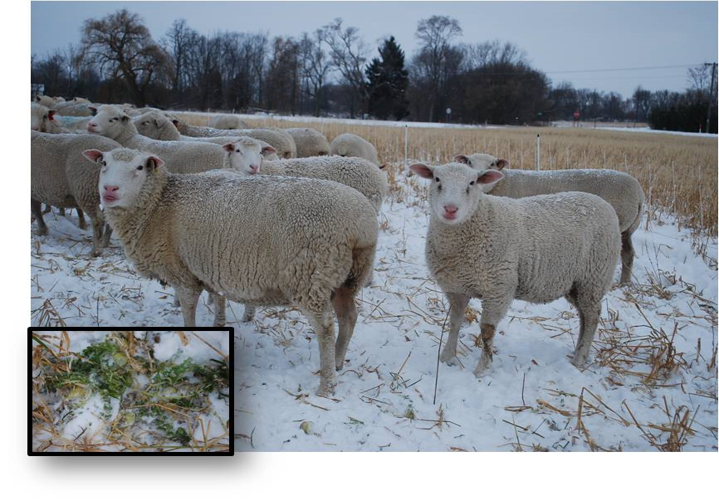 Figure 2. Ewes in mid-pregnancy grazing lush brassica greens and stockpiled oats in late December. The forage water content of this forage is 85%, and this combined with the soft snow provides plenty of water for this group of sheep. The lush aspect of this forage might not be apparent until the snow is uncovered (see inset photo).
Figure 2. Ewes in mid-pregnancy grazing lush brassica greens and stockpiled oats in late December. The forage water content of this forage is 85%, and this combined with the soft snow provides plenty of water for this group of sheep. The lush aspect of this forage might not be apparent until the snow is uncovered (see inset photo).In a practical sense, there are only small windows of time when not providing fluid water becomes an issue in winter grazing in Northern climates. This would be when grazing dry residue such as corn or bean stubble as the temperature drops to below freezing but before snow falls. It is advisable to graze near a fluid water source during these short periods or to stop grazing and feed stored forage where fluid water can be made available. Finally, there are situations when forage water content is so high that is can actually limit the amount of dry feed a sheep can consume and lead to malnutrition! This is a fairly unique scenario, such as when late pregnancy ewes are grazed on brassica tubers (radishes, turnips, rutabagas). Water content of these tubers is very high (>90%). Since dry matter intake of the ewes rarely exceeds 3% of body weight during late pregnancy, it is almost impossible for sheep to eat enough of this watery feed to meet their rising nutrient requirements (an average size ewe might need to eat almost 100 lb of a 95% water crop to meet late-pregnancy dry matter requirements!). Grazing tubers along is just fine for pregnant ewes before late pregnancy, but not advised for those in the last month.
Frozen water sources
Frozen water sources vary in ease of consumption and animal access. Soft snow is easily accessed and consumed by sheep, whereas frozen, packed snow or ice are not. During most winter periods in Michigan, there is enough soft snow available to supplement water present in forage and meet the water needs of ewes that are not lactating or in late pregnancy. In cases when there is a freeze-up following a thaw so that ice and frozen snow forms, both forage access and water access become limiting factors. Animal energy expenditure also goes up as the work harder to walk in muddy conditions and seek feed. Under these conditions, silage feeding may work well to provide both forage and water. If this option is not present, it is best to bring ewes to an area with fluid water access. Allowing ewes to become water- and feed-deprived in cold weather is never advised, even for a few days. The weight loss and stress are extremely costly, and it is sub-standard for sheep welfare. However, the perception that sheep housed outdoors without fluid water are poorly cared is usually incorrect. In fact, sheep grazing quality forage in winter with sufficient water content are many times better off than their housed counterparts due to the benefits of excellent air quality, superior forage quality and exercise.
Summary
- Forage water content meets the needs of most classes of sheep grazing cover crops or stockpiled perennial forage in late fall and winter in many Northern climates with the following exceptions:
- Ewes carrying or rearing multiples in lactation or late pregnancy and rapidly growing young stock
- Consumption of soft snow contributes to water needs but frozen snow/ice can limit water and grazing access and increase energy expenditure
- Dry matter intake can be limited by forage water content under certain conditions:
- Brassica tuber grazing during late pregnancy
- Prolific ewes in general during late pregnancy
- Dry spells during mild weather (late fall or winter)
- Always supply ewes with multiples in late pregnancy and ewes in lactation with supplemental, fluid water.



 Print
Print Email
Email