Fusicoccum canker (constriction canker)
Disease
Fusicoccum canker (constriction canker)
Phomopsis amygdali (Delacr.) Tuset & Portilla
Distribution: Common to all fruit-growing regions in eastern North America; most problematic in warm and humid production regions.
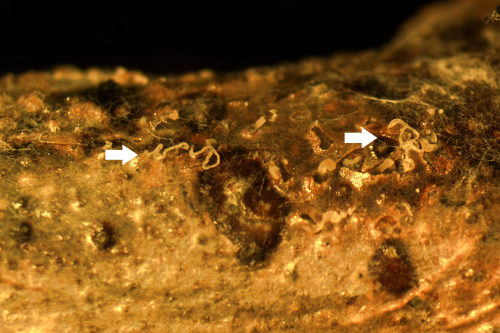
On new shoots, small, reddish brown to dark, oval cankers centered on infected buds or leaf scars, or at the base of current season's twigs are found in early spring (A, B). As lesions enlarge, they develop a necrotic center surrounded by a purplish halo and eventually girdle and kill the branch above the lesion, giving it a blighted appearance. Lesions may be dotted with very tiny black fruiting bodies (pycnidia). Tendrils of conidia are exuded from pycnidia under favorable conditions and can be seen with a hand lens (C). On leaves, large, irregularly shaped brown spots are formed.





 Print
Print Email
Email