Exploring drones with youth
Take the opportunity to introduce youth to the fast-advancing science of drones.
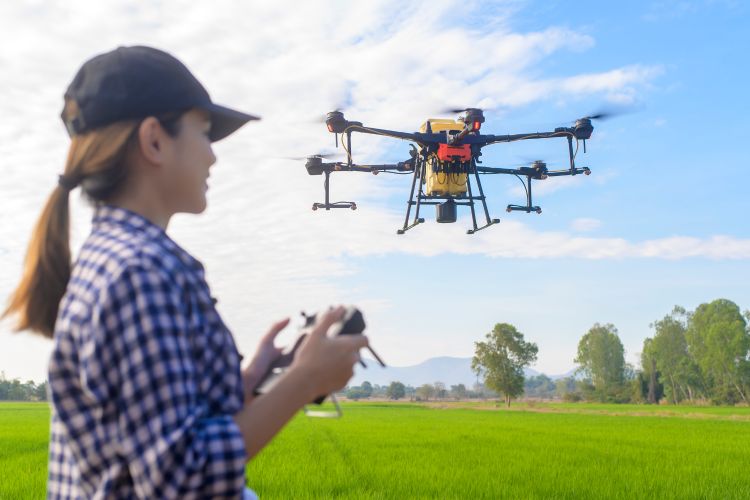

Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) or unmanned aerial systems (UAS), commonly known as drones, are increasingly popular. While the basic parts of a drone are the same – a frame, motors, propellers, battery, flight controller and sensors – their configuration can vary greatly. The two primary types are fixed wing, like an airplane, and multi-rotor. Fixed wing drones can fly higher and have a simpler structure than multi-rotor drones. They are often used for surveys and agriculture because they can cover more than 1,000 acres in a single flight. Multi-rotor drones exist in many configurations, but the most popular is the quadcopter (pictured). A quadcopter can carry a heavier payload than a fixed wing drone. One advantage a multi-rotor drone has over fixed wing is that it can safely take off and land from almost anywhere. A fixed wing drone needs to be launched, usually with a catapult of some type, and without land gear, is damaged when it is landed. To learn more about how drones fly, explore Working Principle and Components of Drone.
Originally used mostly for military purposes, drones are now used for a variety of civilian purposes, such as search and rescue efforts, data analyzing and mapping purposes, as well as delivery of goods. They are used to analyze damage caused by natural disasters; map pest damage, water and nutrient deficiencies in field crops; map and monitor powerlines, pipelines and cell phone towers; and for crime scene investigations, firefighting, weather forecasting, photography, film-making and much more. The list of uses is growing fast and daily as technology advances. Many hobbyists enjoy experimenting with drones. Drones for kids are also easily found online, in toy stores and department stores. They come in a wide range of sizes and prices.
Drones can be a tool to lead young people to science and engineering principles in a fun and hands-on way. Michigan State University Extension 4-H Youth Development has resources available to build youth interest in science, stimulate youth curiosity and creativity, and increase youth critical thinking, decision-making and problem-solving skills. Explore with young people the science of drones through Virginia Cooperative Extension 4-H resources. Youth explore concepts of flight dynamics, engineering design, and principles of flight, remote sensing and computer coding. Youth can explore by creating, coding and “flying” a simulated drone using a Scratch program.
The Scratch program is a free, online computer program designed for youth ages 8 to 16 years old. It introduces youth to coding, allowing them to program by stacking commands like building blocks. Youth learn strategies for solving problems, designing projects and communicating ideas. The simulation gives youth the opportunity to discover practical engineering design solutions to real world problems. At the same time, youth learn about careers related to drone technology. They also become familiar with safety measures and regulations.
Did you know the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulates all aircraft operations, including drones? They require all owners of UAVs weighing between 0.55 and 55 pounds to be registered. For more information, visit the FAA’s Unmanned Aircraft Systems website.
If you are a “drone hobbyist” or are thinking about getting a drone, think about taking it a step further by involving youth. Take the opportunity to introduce youth to the fast-advancing science of drones, as well as safety practices and regulations.



 Print
Print Email
Email