Inactivation of Salmonella Enteritidis PT30 on black peppercorns in thermal treatments with controlled relative humidities
This study demonstrated the potential of using short-time high-RH treatments to control pathogens in low-moisture foods without the need for post-treatment drying.
Abstract
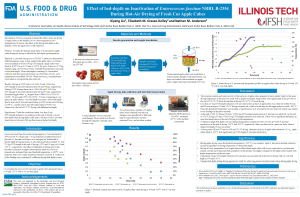
Traditional method utilizes steam to pasteurize low-moisture ingredients like black peppercorns and almonds. Exposure to steam results in direct condensation on the product, unfavorable for a broader range of food ingredients such as dried herbs, fruits, and ground materials. Recent studies on the thermal inactivation of Salmonella in low-moisture foods suggest that the relative humidity in treatment chambers is an important factor, besides temperature, that determines the death rate of bacteria. Thus, thermal treatments with controlled high relative humidity can be an effective method to replace steam pasteurization. No condensation will occur when the products are preheated to above the dew-point temperature of the hot air in the treatment chamber, thus eliminating the need for post-treatment drying. To prove this concept, a special device was developed that preheated samples in a dry environment before exposing them to a controlled relative humidity (RH) at a high temperature. Using this device, the death rate of Salmonella Enteritidis PT30 (S. Enteritidis) in black peppercorns was determined at 80 °C and three different RH levels (60, 70, or 80 %) after the innoculated samples were heated to 78oC. The results indicate that the treatments at 80 °C and 80 % RH for 3 min, 70 % RH for 9 min, and 60 % RH for 25 min caused 5.4 ± 0.2, 6.2 ± 0.6, and 6.1 ± 1.0 log reductions, respectively. No condensation was observed on all of the treated samples. The moisture content (wet basis) of fully pasteurized (5-log reduction) black peppercorns at 60, 70, and 80 %RH reduced from 9.7 ± 0.4 % (untreated) to 8.7 ± 0.5 %, 9.2 ± 0.4 %, and 9.2 ± 0.2 %, respectively, indicating that post-drying is not required after the treatments. This study demonstrated the potential of using short-time high-RH treatments to control pathogens in low-moisture foods without the need for post-treatment drying.



 Print
Print Email
Email