Yeast-Associated Asthma
Asthma affects 339 million people globally and the rate of increase is about 50% each decade.
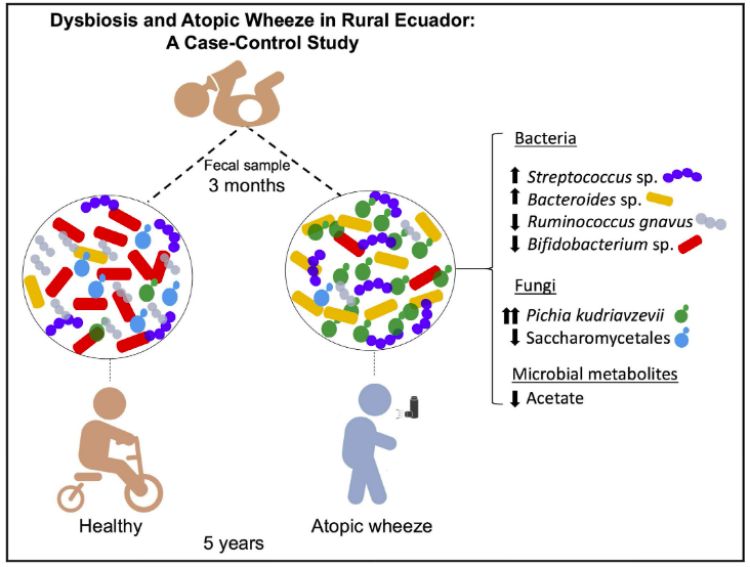
Asthma affects 339 million people globally and the rate of increase is about 50% each decade. A study on the relationship between the gut microbiome and risk for asthma was conducted in Ecuador. Researchers analyzed the gut of babies, looking for microbes that were associated with atopic wheeze at 5 years old, an early indicator of asthma in children.
A similar study in Canada looked only at bacteria, but the results from this study did not align, likely due to environmental and cultural differences. This study in Ecuador also looked at the fungal biome.
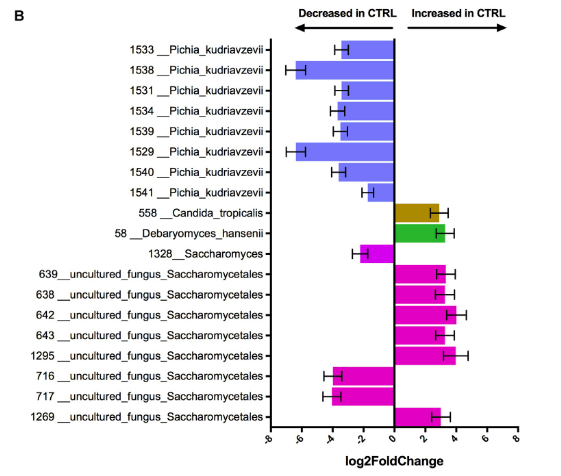
Unexpectedly, the researchers found that a single yeast was highly correlated with an increased risk of asthma: Pichia kudriavzevii, teleomorph of Candida krusei.
Using the 18S rRNA marker gene to profile microbiomes, the found that general fungal dysbiosis in babies was also correlated. In healthy children, filamentous fungi and yeasts comprise a much smaller proportion than in at-risk children.
Sources:



 Print
Print Email
Email



