Jackson
The federal government redline mapped Jackson in the late 1930s. Consistent with the requirements of the government Underwriting Manual, the redline mapping specifically targeted residents of color, deeming their neighborhoods as “hazardous” to investment because they had residents of color or were even near residents of color. The original redlining map is shown below. While HOLC did not itself implement these redlining maps, it promoted these practices and showed private industry groups and the FHA how to reproduce these maps. We also have a map overlaying the original HOLC boundaries on present-day segregation, which starkly show the continued effects of these racist practices. The strong visual connection between original HOLC grades and present-day racial segregation, shows a legacy of redline mapping on present-day outcomes.
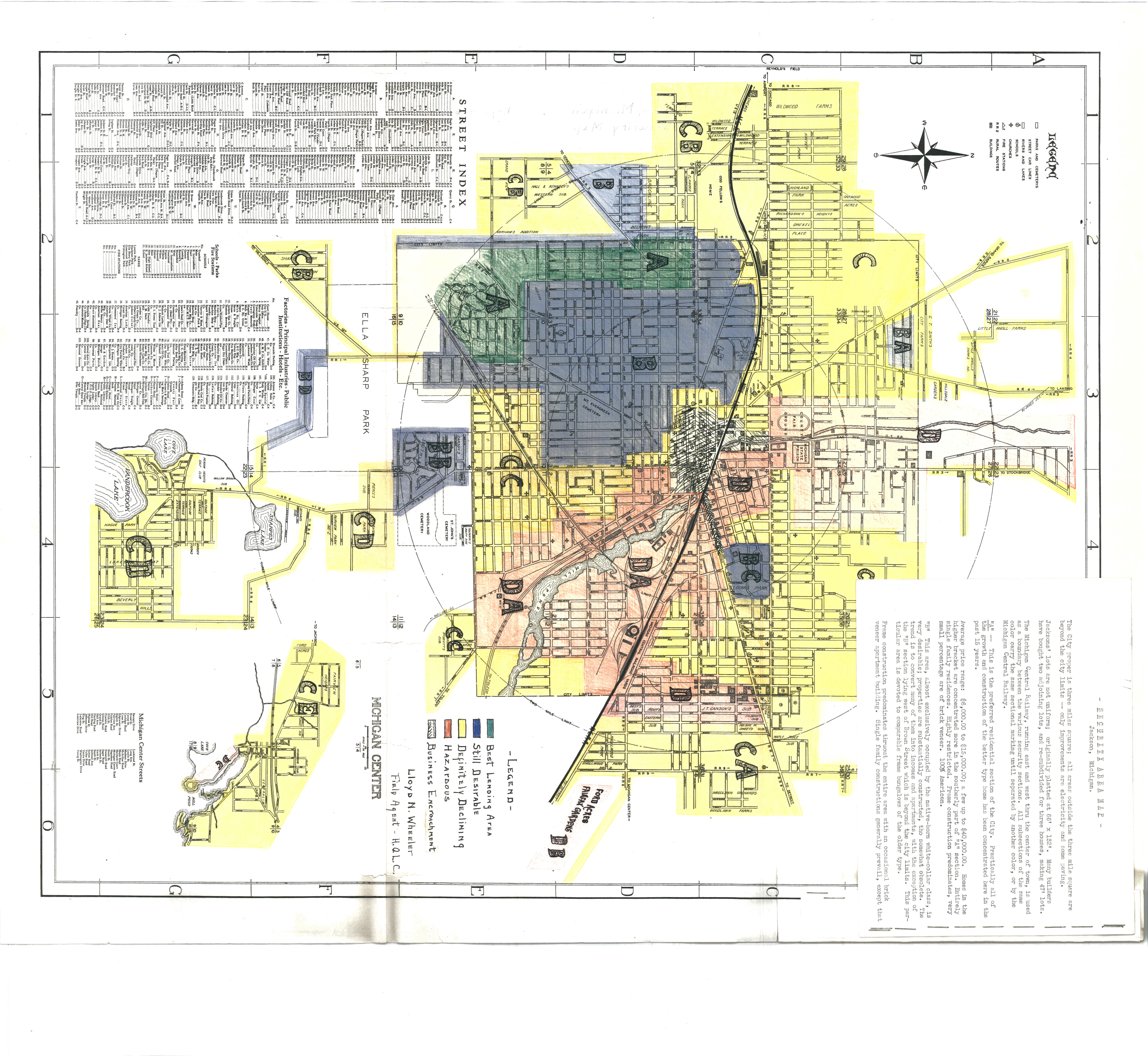
Jackson Neighborhood Grading Justifications
The racist language and explanations below are quoted from the “Area Description Files” filled out by government appraisers. The language and justifications are coarse and offensive. Nonetheless, it is important to remember our past in all of its coarseness is offensiveness to fully understand the context that we confront today, especially when developing equitable housing policies.
Appraiser Area Description Files for Jackson have not been found in their entirety and may not still exist. Some notes on the map, however, indicate that appraisers graded areas green because there were “100% American,” i.e., White, and graded neighborhoods blue because it was “almost exclusively” occupied by “native-born white-collar class.” “Single family constructions” are emphasized as a tool of exclusion.
The Legacy of Redlining in Jackson
We overlay the historical HOLC “redlining” map on present-day demographic data to show the persistence and continued relevance of these racist policies on present-day segregation. We mirror the racist HOLC color gradation to help visualize the continued segregation, as a lasting impact of redlining.
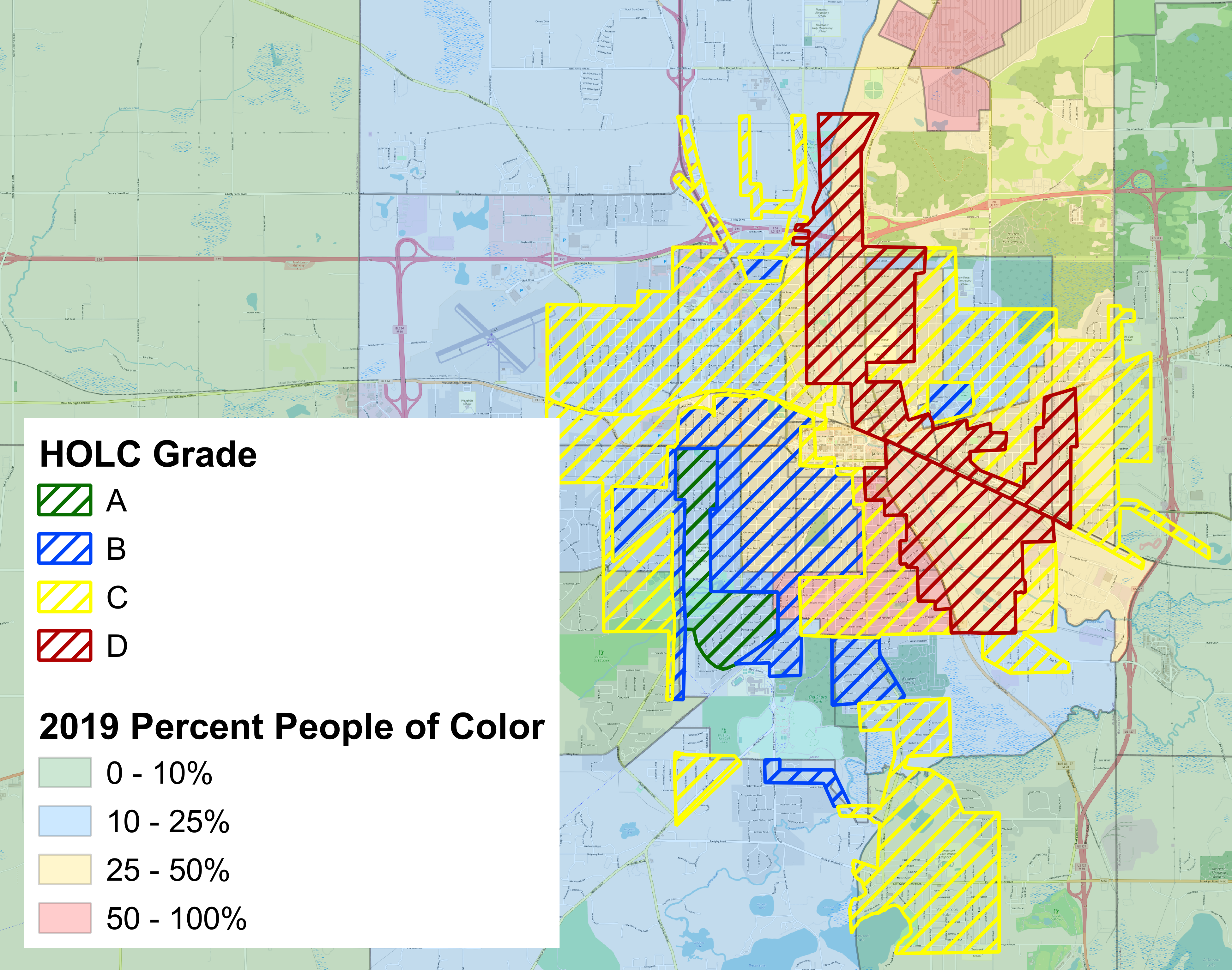
Higher segregation is associated with lower incomes, lower educational attainment, more crime, worse health outcomes, and higher inequality. But segregation is not the only lasting impact of redlining in Michigan Cities, or in Jackson. Researchers have shown that redlining also directly reduced many of these outcomes.
This research was conducted by Michigan State University Assistant Professor and Extension Specialist Craig Wesley Carpenter, Ph.D. (@DrCWCarpenter or cwcarp@msu.edu).



 Print
Print Email
Email