Fruit Pest and Beneficial Listing Widget
Apples Insect
-
Alternaria blotch
Disease
The disease primarily affects the foliage, causing circular, necrotic lesions with a light brown interior that later become surrounded by a darker purplish halo.
-
Alternaria fruit rot
Disease
The disease appears as velvety dark green to black, circular, sunken lesions on mature fruit; the infected tissue is firm and brown. Disease is typically associated with over-ripe or damaged fruit, or fruit held in storage.
-
American hawthorn rust
Disease
Attacks only the leaves of apple and pear; affects the apple varieties McIntosh and Cortland in particular.
-
American plum borer
Insect
The adult is a light grayish brown moth with reddish brown forewings marked by wavy black and brown vertical bands about two-thirds the distance from the base.
-
Apple (Lyonetia) leafminer
Insect
The adult has narrow white forewings with extensive gray-black and brown markings apically wing margins are fringed with long hairs. The larva is whitish and generally concealed within the leaf mine.
-
Apple anthracnose
Disease
Branch lesions first appear as small, circular spots that are purple or red when wet. As lesions enlarge, they become elliptical, sunken and turn orange to brown. A distinct margin develops between healthy and diseased tissue, which eventually causes the bark to crack around the infected area.
-
Apple latent viruses
Disease
Latent viruses are viruses that survive in their host without causing symptoms. These viruses are transmitted when a virus-infected scion is grafted onto a susceptible rootstock.
-
Apple leaf (curling) midge
Insect
The adult is a tiny dark brown fly, and the larva is a yellow-white maggot with a reddish tinge.
-
Apple maggot
Insect
Adults are black flies with three or four white cross bands on the abdomen, a prominent white spot at the posterior end of the thorax, and the wings are marked with black bands in the shape of an "F".
-
Apple mosaic virus
Disease
Young leaves develop pale to bright cream-colored spots, blotches, bandings or patterns as they expand in the spring. These turn brown and become necrotic as they age and premature defoliation may occur when infection is severe.
-
Apple pith moth
Insect
Head of adult is covered with white scales; forewings are narrow, mostly black or dark brown with white marks and usually with an irregular faint, rusty yellow line in the middle, and with two prominent black scale tufts.
-
-
Apple rust mite
Insect
The vermiform adult has two pairs of legs at the front of its body. Brownish yellow in color, they are invisible to the naked eye, requiring a minimum magnification of 15X to be observed.
-
Apple scab
Disease
On leaves, young lesions are velvety brown to olive green with indistinct margins, and will often not be readily noticeable until after petal fall in commercial orchards.
-
Apple seed chalcid
Insect
Adult is a small, dark wasp with a bright green head, thorax and abdomen with coppery or bronze metallic reflections, brownish yellow legs, clear hyaline wings, and a long ovipositor.
-
Apple sucker
Insect
Adult resembles a miniature cicada, greenish yellow to yellow in color but sometimes containing reds or browns, with eyes pale green to reddish brown, and long slender antennae; wings are transparent and iridescent.
-
Apple union necrosis and decline
Disease
AUND is due to an incompatibility at the graft union where a resistant scion is grafted onto a susceptible, but tolerant rootstock, most commonly MM.106.
-
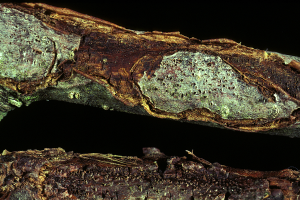
Armillaria root rot
Disease
The bark at the crown and roots sloughs off easily, exposing the dense white growth of the fungus. The growth extends in a fan-like pattern underneath the bark. Black shoestring-like strands may be obvious on the surface of the bark.
-
Bitter pit and cork spot
Disease
Small, green to purplish to light brown, slightly sunken lesions appear on the surface of mature fruit. Individual lesions on the fruit surface are dry and do not extend deep into the fruit; however, cutting into the fruit can reveal numerous internal lesions.
-
Bitter rot
Disease
Bitter rot appears on young fruit as small, circular brown lesions. Lesions expand rapidly and radially under wet and warm conditions. As they age, they turn darker brown and become sunken.
-
Black pox of apple (blister canker of pear)
Disease
On apple, conical, smooth, shiny black swellings are evident on current season's growth. As lesions age, they become ovoid with raised borders. On leaves, lesions begin as small, circular green spots surrounded by a red halo.
-
Black rot (Blossom end rot, Frogeye leaf spot)
Disease
Fruit infections that occur early in the season appear at the calyx end and typically develop into blossom end rot that may not appear until the fruit begin to mature.
-
Blister spot
Disease
Lesions begin as small, darkened, water-soaked areas, generally around lenticels and typically on the lower half of the apple.
-
Blue mold
Disease
Blue mold enters the fruit through wounds, stem-end invasion, or as a core rot. Infection is first visible as a soft and sunken, yellow to pale-brown circular lesion on the surface of the fruit.
-
Brooks fruit spot
Disease
Appears as irregular, slightly sunken dark green lesions on immature fruit.
-
Brown marmorated stink bug
Insect
Brown marmorated stink bug adults are shield-shaped, with mottled brown coloration on the upper and lower surface. They can be distinguished by lighter bands on antennae and they have darker bands on the membrane part of the front wings.
-
Brown stink bug
Insect
Stink bug adults have a broad, flattened, shield-shaped body and a narrow head. The brown stink bug is brown to grayish-brown and slightly speckled.
-
Buffalo treehopper
Insect
The pale green adult exhibits a large thorax with two "horns" and a long posterior wedge-shaped body. The cream-colored eggs are laid in a groove on the tree bark, where they overwinter.
-
Calyx end rot
Disease
Symptoms begin at the calyx end of the fruit, causing a reddish discoloration at the site of infection. The rot is at first soft, but eventually dries out, turning tan to brown with a red border.
-
Cedar apple rust
Disease
On leaves, the disease appears on the upper surface as small, faint, yellow spots shortly after the appearance of active cedar galls found on the alternate host for this fungus, the red cedar.
-
Cherry fruitworm
Insect
The adult is a small, brownish gray moth with a median gray band on the forewings and a dark spot at the base of the hind wings. Although whitish gray with a black head when young, the larva eventually becomes pink tinted, with a brownish tan head.
-
Cigar casebearer
Insect
Adult is dark gray with fringed wings. The small yellowish larva of the cigar casebearer has a black head and builds and hides in a cigar-shaped shelter that it carries with it while feeding or attaches to leaves and branches of apple trees.
-
Click beetles
Insect
The click beetle is dark-colored its body is hard and elongated it has a characteristic pair of spurs and sometimes colorful markings on its thorax.
-
Climbing cutworms
Insect
Adults are dark brown or grayish colored moths. Larvae tend to be smooth caterpillars with few hairs, brown or black head capsules, and bodies a dull gray-brown background color with stripes, spots, or dark brown, black, yellow or white splotches.
-
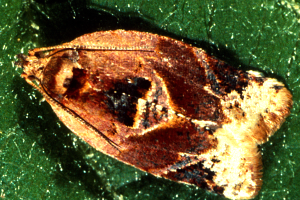
Codling moth
Insect
The adult's forewings are striped with fine brown-gray lines and a distinctive bronze to brown-black oval spot at the tip. Eggs are laid on the leaves or fruit.
-
Comstock mealybug
Insect
Adult females and nymphs are generally similar in appearance, having an elongate-oval shape, no wings, a many-segmented body and well-developed legs.
-
Crown gall
Disease
Infected trees are often stunted and produce small, chlorotic leaves. Spherical to elongated swellings along the roots or on the trunk just above the soil line is the primary symptom.
-
Dock sawfly
Insect
The adult is bluish black with red legs. The larva is a smooth velvety green worm with white legs and a dark head.
-
Dogwood borer
Insect
The adult is bluish black with yellow bands and has clear wings, resembling a wasp. Larva is creamy white to pink with a sclerotized reddish head.
-
Dry eye rot (blossom end rot)
Disease
Symptoms begin at the calyx end of the fruit, causing a reddish discoloration at the site of infection. The rot is at first soft, but eventually dries out, turning tan to brown with a red border.
-
Dusky stink bug
Insect
Stink bug adults have a broad, flattened, shield-shaped body and a narrow head. The dusky stink bug is dark brown, with sharp shoulder projections.
-
Eastern tent caterpillar
Insect
The adult is reddish brown with two white, transverse-parallel bands. Masses of shiny black eggs are laid in a ring around twigs. Larvae have long silky hairs on their body and a yellow line on their back.
-
European apple sawfly
Insect
The adult looks similar to a small, orange-brown wasp with the ventral side and legs orange in color. It has transparent wings with many veins. The egg, oval and translucent, is inserted into the receptacle of the flower.
-
European corn borer
Insect
Adult is a pale yellowish brown moth with irregular darker bands running in wavy lines across wings male is distinctly darker than the female.
-
European earwig
Insect
The European earwig is dark brown with an elongated body, equipped with pincer-like forceps at the rear of the abdomen. The short elytra do not entirely cover the abdomen.
-
European fruit lecanium (Brown apricot scale)
Insect
The adult female scale is nearly hemispherical and shiny brown, with several ridges along the back. Nymphs are light colored.
-
European fruit scale
Insect
The female is immobile and covered with a circular waxy shell that becomes dark gray over time and is elevated at the center. The adult male is brownish red with an elongated abdomen, long antennae and wings.
-
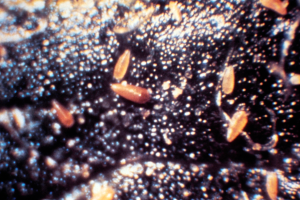
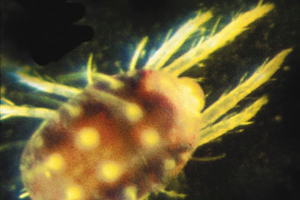
European red mite
Insect
Adult female European red mites are less than 0.5 mm and dark red with eight legs. Adult males are smaller than the females and have a pointed abdomen. Males are usually dull green to brown.
-
Eyespotted bud moth
Insect
Adult forewings are bluish gray with a central cream-colored band and black spots. The chocolate brown larva has a black head and thoracic shield.
-
Fall webworm
Insect
Adult is a white moth with dark spots on the wings, which may be less distinct in northern specimens. The pale yellow larva has a dark head and dark tubercles with clumps of hairs.
-
Fire blight
Disease
Blossom blight occurs in the spring. Infected blossoms first exhibit a water soaking, followed by wilting and their eventually turning brown on apple and nearly black on pear. Individual flowers or the entire cluster may be affected.
-
Flatheaded appletree borer
Insect
The adult is a short-horned beetle, flattened above, with short antennae and large conspicuous eyes. The upper surface of the body is dark metallic brown with slightly patterned wing covers.
-
Flyspeck
Disease
Sooty blotch and flyspeck are found together on the same fruit and affect only the epidermal layer of the fruit. Flyspeck colonies appear as distinct groupings of shiny, black fungal bodies on the surface of the fruit.
-
Forbes scale
Insect
Round or elongate gray scale with a raised reddish area in the center, which distinguishes it from the San Jose scale.
-
Forest tent caterpillar
Insect
Adults are reddish brown with two brown, transverse-parallel bands. Masses of shiny black eggs are laid in a ring around twigs. Larvae have long silky hairs on their body and a row of elongated spots along the back.
-
Fruittree leafroller
Insect
The adult is red-brown with mottling. The translucent green caterpillar has a reddish to dark brown head and an amber to pale green thoracic shield edged with brown.
-
Gray mold
Disease
Lesions usually start at the calyx or stem end of the fruit or at wound sites as small water-soaked areas. As lesions age, they enlarge, turning from grayish-brown to light brown, and eventually to a darker brown.
-
Green June beetle
Insect
The adult is velvet green dorsally with yellow-orange margins on the elytra. Ventrally it is a shiny metallic green mixed with orangish yellow. The larva is a large, C-shaped grub that lives in the soil and is not found in the trees.
-
Green pug
Insect
The adult is a grayish moth with mottled or scalloped dark striations toward the wing margins. The larva is a green inchworm with a dark head and a dark reddish brown dorsal mid-line present in later instars.
-
Green stink bug
Insect
Stink bug adults have a broad, flattened, shield-shaped body and a narrow head. The green stink bug is uniformly grass-green.
-
Gypsy moth
Insect
The adult male is brownish and marked with blackish zigzag lines. The adult female is whitish with brown transverse zigzag stripes and does not fly. The masses of oval and yellow eggs are laid on the trunk of trees and covered with hair left by the female.
-
Hawthorn dark bug
Insect
The young adult is black with red wing markings, which disappear a few days after it metamorphoses into an adult.
-
Humped green fruitworm
Insect
Adult's forewings are gray and marked with light and dark areas for 2/3 of their length the outer 1/3 is a lighter gray.
-
Japanese beetle
Insect
Japanese beetles can be present from June through September. Japanese beetle adults are metallic green or greenish bronze with reddish wing covers and several white spots near the abdomen tip and along the sides. Larvae are larger C-shaped grubs that live in the soil.
-
Leaf weevils
Insect
Leaf weevils are green or brown curculios with a metallic appearance. Their antennae are borne on the snout.
-
Lesser appleworm
Insect
The adult is a small gray moth with distinct small orange bands or patches on the wings; some blue is also evident in newly emerged specimens.
-
Mineola moth (Destructive pruneworm)
Insect
Adult is a bluish gray moth that assumes a wedge shape when at rest. It has a transverse broad white stripe bordered by a smaller reddish brown stripe in the middle of the forewings a smaller set of similar bands occur near the posterior edge.
-
Moldy core and core rot
Disease
Moldy core is associated with several different fungi. Infection is initiated at the calyx end and the fungi proceed to grow inward into the carpel tissue or locules and cause a core rot.
-
Mucor Rot
Disease
Infected tissue appears light brown, soft, and watery. The infection usually develops at wound sites, at the calyx end, or at the stem end of the fruit.
-
Mullein plant bug
Beneficial
Adult is grayish green with black spots on the legs. The nymph resembles an apple aphid or a white apple leafhopper and is solitary, very mobile and lacks cornicles.
-
Necrotic leaf blotch
Disease
Medium to large, irregular necrotic lesions occur on the foliage of mature leaves during mid- to late summer. The remaining green tissue generally turns yellow shortly after the appearance of symptoms.
-
Nectria canker
Disease
Cankers are often associated with nodes, often appearing as elliptical sunken areas. Sometimes callus production stops fungal invasion and cankers die by season's end.
-
Nectria twig blight
Disease
Typically, small cankers can be found girdling the base of cluster buds that bore fruit the previous year. This leads to the wilting and dying of leaves and twigs of current season's growth.
-
Obliquebanded leafroller
Insect
Adult wings are beige, tinged with red. Forewings are crossed with oblique brown bands. The female is larger than the male. The green eggs are laid in masses on the upper surface of leaves.
-
Oriental fruit moth
Insect
The adult is a small moth with dark gray mottled wings that lighten somewhat at the outer edges. The larva is dirty white to pinkish with a reddish brown head and an anal comb.
-
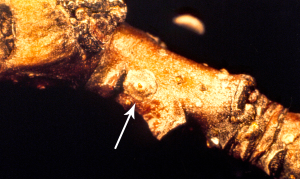
Oystershell scale
Insect
The adult female remains immobile under a small brown scale in the shape of an oyster shell attached to the bark of branches. The white and oval eggs are laid inside the scale and crawlers emerge in the spring during the petal fall stage of apple.
-
Pale apple leafroller
Insect
The adult is elongated and dull gray. The larva is creamy white with an amber head, which turns black in the penultimate instar.
-
Pear plant bug (Green apple bug)
Insect
The adult pear plant bug is brownish yellow with two dark bands on the thorax and the extremities of its anterior wings are yellowish in color.
-
Pear thrips
Insect
Adult is slender and brown, with short antennae and a swelling behind the head; the wings are long and narrow, with fringes of long hairs.
-
Perennial canker of apple and pear
Disease
Branch lesions are elliptical, sunken, and orange, purple, or brown in color. A raised layer of callus tissue forms around the infected tissue to isolate the diseased tissue.
-
Periodical cicada
Insect
Adults are wedge-shaped, nearly black, with red eyes and red-orange wing veins. The clear wings are held tent-like over the body.
-
Phytophthora root, crown, and collar rot
Disease
Crown and collar rot are often and mistakenly used interchangeably. Collar rot refers to infection that affects the bark tissue of the scion portion of the tree at or just below the soil line, whereas crown rot affects the bark tissue of the rootstock portion of the tree.
-
Pistol casebearer
Insect
Adult is dark gray with fringed wings. The pistol casebearer appears similar to a cigar casebearer: a small, yellowish larva with a black head that builds and hides in a shelter.
-
Plum curculio
Insect
The adult is mottled grayish black and brown. Its head is prolonged into a large but short snout that bears antennae. Each elytron has a series of humps with the 2nd and 3rd pairs separated by a clear transverse band.
-
Potato leafhopper
Insect
All leafhopper species feed on the undersides of leaves, puncturing cells and sucking out the contents. In general, juice grape (labrusca) varieties are much more tolerant of leafhoppers than hybrid or vinifera varieties.
-
Powdery mildew of apple and pear
Disease
The fungus overwinters in leaf buds and sometimes flower buds. Mycelium develops rapidly on unfolding leaves and appears as white, felt-like patches or as a solid mat on the upper or undersurface of the leaf.
-
Prionus borers
Insect
Adults are robust, broad, somewhat flattened blackish to reddish brown beetles with antennae roughly half the length of their bodies.
-
Quince rust
Disease
Attacks only the fruit of apple and pear. Symptoms begin as a purplish lesion, usually appearing on the calyx end of the fruit. As the disease progresses, the entire calyx end becomes blistered and deformed. Tube-like structures eventually form and produce powdery, bright orange spores.
-
Redbanded leafroller
Insect
The adult's forewings are grayish brown with a subtle dark red and brown oblique band. The larva is pale green with a yellow or green head.
-
Redhumped caterpillar
Insect
The adult is a grayish brown moth. The larva is yellow with a red head and is lined longitudinally with orangish, black, and white stripes.
-
Replant disorders
Disease
In general, trees suffering from replant disease show slow and uneven growth within the first three years of planting. Both specific and non-specific replant disorders are known.
-
Root-lesion nematode
Disease
Root-lesion nematodes are microscopic, migratory endoparasites that feed on the root systems of many crops. Affected trees appear stunted, may exhibit chlorosis or yellowing of the leaves, and have poor yields; young trees may be killed.
-
Rose chafer
Insect
The rose chafer is a light tan beetle with a darker brown head and long legs. It is about 12 mm long. There is one generation per year.
-
Rosy apple aphid
Insect
Populations arise from the overwintered stem mothers, which are wingless and purplish in color, and form into colonies of rosy-purple nymphs with dark cornicles.
-
Roundheaded appletree borer
Insect
Adult has a hard, elongated body, with white and brown longitudinal stripes and long antennae. The larva is a fleshy, cream-colored legless grub with a dark brown head, blackish mandibles.
-
San Jose scale
Insect
Adult males are minute, winged insects about 1 mm long and golden brown with a reddish tinge. Scales may be either disk-shaped or oval, and are composed of concentric rings of gray-brown wax radiating from a tiny white knob.
-
Shothole borer
Insect
The adult is stocky with a hard black body and antennae, leg segments and tips of elytra reddish brown; its head is not visible from above.
-
Silver leaf
Disease
Silvering of the foliage is the characteristic symptom. At first, silvering may be associated with only one or two major branches, but eventually the entire tree becomes silvery in appearance. When infection is severe the leaves may curl upward.
-
Skeletonizers
Insect
The adults of the skeletonizers are brown and short, with transverse bands on each forewing. The larvae are yellow to pale green with numerous hairy discs on each segment of the body.
-
Snowy tree cricket
Insect
Adult somewhat resembles a field cricket, but is pale green in color and has a longer, more slender body and smaller head. Antennae are much longer than the body; males have stiff veins in their flat wings.
-
Sooty blotch
Disease
Sooty blotch and flyspeck are found together on the same fruit and affect only the epidermal layer of the fruit. Sooty blotch appears as various shades of olive-green on the surface of the fruit.
-
Southern blight
Disease
Trees attacked by the fungus show a general decline. In the early phase of disease, a dense mat or web of white mycelium is evident at the base of the tree.
-
Sparganothis fruitworm
Insect
Adult is a vivid yellow moth with grayish magenta V-shaped marks on the forewings and reddish orange lace-like markings. Larvae are pale green with yellowish-green head.
-
Green fruitworm
Insect
Immature larvae of the green fruitworm (GFW) feed on flower buds and new foliage.
-
Speckled green fruitworm
Insect
The adult is grayish beige with two purplish gray spots on its wings and a hairy thorax. The eggs are laid on the upper surface of the leaves.
-
Spirea aphid
Insect
The eggs are oval and shiny black. The adults and nymphs are olive-green with brown-black legs, antennae, and cornicles. They live in colonies.
-
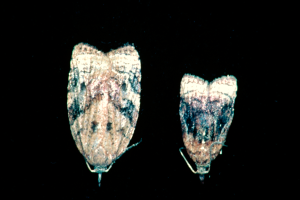
Spotted tentiform leafminer
Insect
The adult is a tiny beige moth with heavily fringed wings striped with golden brown and white bands. Eggs are laid individually on the undersurface of the leaves.
-
Spring cankerworm
Insect
The adult male is gray and has winding lines on its forewings the female has stumpy gray wings. The larva is pale green to dark brown with two yellow longitudinal bands on the sides. It moves in a looping inchworm fashion.
-
Tarnished plant bug
Insect
The adult is brown and the extremities of its wings are translucent with a cream-colored scutellum on its back. The nymph is pale green; from the 3rd nymphal stage, it has five black points on the back.
-
Tufted apple bud moth
Insect
Adult is an inconspicuous moth, varying from mottled gray at the wing base to brown at the wing tip, with a lighter colored margin along the wing's leading edge. Two or three groups of tufted scales can be seen on the top of the wings.
-
Twospotted spider mite
Insect
Adult and nymphal mites are yellowish to pale green with a dorsal pair of apparent dark "spots". Males are smaller than females and have a pointed abdomen. The female takes on an orange tinge in the fall.
-
Variegated leafroller
Insect
Adult is grayish magenta with dark brown bands on the middle and end of the forewing. Larvae are pale green with yellowish green heads.
-
Verticillium wilt
Disease
Leaves wilted or browned on one or several branches, often remaining attached; the rest of the tree appears healthy. Young trees are often killed by infection.
-
White apple leafhopper
Insect
Adults are creamy white with short antennae, translucent wings, and a long wedge-shaped body. Usually found on the underside of leaves, they jump and fly with great agility. Nymphs are yellowish, wingless and very mobile; they generally move in a back-and-forth motion.
-
White rot
Disease
Fruit lesions become visible 4–6 weeks before harvest, and appear as small, circular, slightly sunken tan to brown spots, sometimes surrounded by a red halo on yellow-skinned fruit.
-
Widestriped green fruitworm
Insect
The adult has bluish or steel gray wings marked with inconspicuous mottled patches.
-
Winter moth
Insect
Adult male has grayish-brown wings; the female has remnants of wings and so cannot fly. This, in combination with the female's large body, makes the legs appear to be long, and gives her the superficial appearance of a spider.
-
Woolly apple aphid
Insect
The colonies of reddish brown adults and nymphs produce waxy secretions, which resemble small tufts of wool or cotton batting. The aphids are without cornicles, possessing only abdominal pores.

















































































































 Print
Print Email
Email